Preparing Youth for Agri-preneurship Development
Agriculture has long been the backbone of India’s economy, sustaining millions of livelihoods and delivering 18.4% (https://www.upag.gov.in/dash-reports/gvaagri) of the nation’s Gross Value Added (GVA) in recent years. It remains the largest source of employment, especially in rural areas. Yet, the sector faces persistent and emerging challenges such as climate change, land degradation, fragmented small land holdings, limited technological integration in farming, optimizing water use, harnessing monsoon rains, over-reliance on monsoons, crop and livestock diseases, post-harvest losses, and highly volatile market prices. Addressing these complex issues requires a workforce that is not only skilled and knowledgeable but also innovative and entrepreneurial underscoring the vital role of agricultural education in securing the sector’s future profitability and sustainability. There is the need for technology integration and entrepreneurship in agriculture to address challenges such as population growth and decreasing land holdings. Also, there is a need to prepare students for future scenarios with limited land availability and the importance of diversifying agricultural education to include animal husbandry. The education system should shift focus from producing job seekers to nurturing job creators through entrepreneurship and startup-ecosystem training. A brainstorming session on “Preparing Future-Ready Youths for Entrepreneurship Development in Agriculture” was organized to stimulate policy innovations and also Institutional reforms in academics, paving way in building students for more meaningful lives and work roles and enabling economic independence of learners capable of global competence. This would encourage higher agricultural education (HAE) Institutions to shape new generation youth in agriculture and allied fields and motivate all stakeholders, educationists, policy makers in contributing to fulfilling the aspiration of the Viksit Bharat.
- Published in AGRIPRENEURSHIP, POLICY, YOUTH
WOMEN AT THE HELM: Navigating the Digital Landscape of Agriculture
The study identified two types of enterprises led by women in the digital ecosystem: digitech enterprises, often founded by women with a background in technology, and digitally enabled enterprises, leveraging various digital technologies to promote their businesses. The majority of women entrepreneurs operate digitally enabled enterprises, reflecting the tech-driven nature of modern agribusiness.
This compilation of interviews illustrates how digital innovations support women agripreneurs in India, showcasing their entrepreneurial journeys, aspirations, challenges, and strategies to overcome these challenges through digital interventions and other forms of support. It is intended to benefit those supporting women agripreneurs, particularly within India’s agribusiness incubation centres, offering valuable insights and lessons for leveraging digital innovations to enhance enterprise performance. We sincerely believe that each of these life stories will also inspire several budding women agripreneurs and help them assess their digital capacity gaps and take steps to address these.
- Published in POLICY
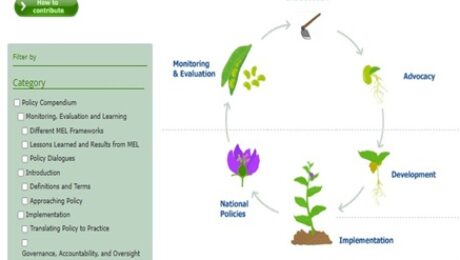
GFRAS Policy Compendium
The Policy Compendium is a tool that contributes to filling the gap between the rural advisory services (RAS) policy environment and RAS efforts in the field. It helps direct decisions and facilitate successful policy processes and outcomes in extension and advisory services by making knowledge accessible, fostering synergies and promoting policy processes to improve RAS and rural development.
- Published in POLICY
State of Agricultural Extension reforms in India and the need of convergence
Extension reforms play a significant role in catalysing the extant policies and provisions that are affecting the extension service across India. Although the country has seen a series of reforms in the past seven decades, the changing contours of agriculture over the years demand new sets of interventions and reform measures. Regimes in the past decades have brought a series of measures to strengthen the extension system. The present study found that the most of the reforms were concentrated on a single theme and even the multiple reforms were overlapping with similar mandates. This resulted in poor performance and poor accessibility to the needy households. Moreover, during the pandemic the existing system reforms showed a fair amount of refinement. Therefore, the study highlights the importance of convergence across common themes of various interventions brought in to enhance the extension services.
- Published in EXTENSION AND INNOVATION, POLICY
School Food and Nutrition – Global Action Plan 2022–2026
This publication is the result of a collective effort, and includes contributions from relevant technical units of FAO across global, regional and country levels. The development of this plan follows the publication and dissemination of the Organization’s School Food and Nutrition Framework, and provides the implementation roadmap to attain its expected results.
The School food and nutrition – Global action plan seeks to consolidate and guide FAO’s synergistic efforts, setting out priority and concrete outputs to be achieved by 2026. Key activities are presented in the plan and organized according to the following action areas: 1. promote the uptake of and investment in holistic approaches to school food and nutrition (SFN); 2. enhance capacities to design, implement and monitor effective SFN interventions; 3. strengthen policy and legal frameworks that enable SFN implementation; and 4. mobilize resources for ensuring regular and better support to countries. These have been prioritized based on identified gaps and needs, and considering the Organization’s technical competence and organizational comparative advantage. Such activities are meant to be adapted, contextualized and implemented according to regional and national priorities.
READ MORE
- Published in POLICY
Research Series 73: Food systems and rural wellbeing: challenges and opportunities
This paper provides a framework for assessing the dynamics of rural wellbeing and food systems change. It provides a synthesis of over 840 recommendations made in recent international reports on the linkages between food systems and rural development. It also looks at the viability of small-scale farming and the diversification of livelihood options needed to overcome rural poverty and inequality.
- Published in POLICY
Repurposing Agricultural Policies and Support
The report finds that repurposing a portion of government spending on agriculture each year to develop and disseminate more emission-efficient technologies for crops and livestock could reduce overall emissions from agriculture by more than 40 percent. Meanwhile, millions of hectares of land could be restored to natural habitats. The economic payoffs to this type of repurposing would be large. Redirecting about $70 billion a year, equivalent to one percent of global agricultural output, would yield a net benefit of over $2 trillion in 20 years.
- Published in POLICY
Increasing stakeholder participation in forest law reform process-Case studies from FAO-EU FLEGT Programme
The FAO-EU FLEGT Programme is carrying out an experience capitalization exercise to collect, analyse and share experiences, good practices and lessons learned during the implementation of the Phase III of the Programme. As a part of this effort, the Programme agreed to support the project entitled “Increasing Stakeholder Participation in Forest Law Reform Process: Case Studies from FAO-EU FLEGT Programme”. This project, carried out and co-financed by ClientEarth, includes a review of nine projects that focused on increasing stakeholder participation in legal reform processes in the following countries: the Republic of Congo, Cote d’Ivoire, Liberia, Malaysia, Myanmar and the Philippines. The publication includes the aggregate findings of the six focus countries, general analysis and recommendations.
- Published in POLICY
Tackling inequalities in public service coverage to “build forward better” for the rural poor
this policy brief specifically focuses on tackling rural inequalities in public service coverage. Drawing evidence from across sectoral domains, the policy brief explores the manifestations of, causes of, and means to redress inequitable public service coverage within rural areas as well as between rural and urban areas. The primary target audiences for this policy brief are policy-makers, planners and development partners.
- Published in POLICY
Strengthening Local Self Governance in Jharkhand
This document is prepared to illustrate the process of implementation of GSA from December 2017 to November 2020 in Jharkhand undertaken by PHIA and partner organisations with funding support from Azim Premji Philanthropic Initiative. This document is prepared as a best practice for knowledge sharing and as a tool for practitioners and policy makers to replicate and scale the initiative in a similar context. It is a step-by-step guide for promoting the agenda of local self-governance and boosting local democracy by following a systemic process and set of interventions.
- Published in POLICY