A decision guide for rural advisory methods
This decision guide is intended to help extension professionals and their organizations make informed decisions about which extension method and approach to use for providing information, technologies and services to rural producers and to facilitate interactions and knowledge flow. Expected users include field-based rural advisors, extension managers and programme planners.
- Published in CONCEPTS AND PRACTICES, GUIDE/TOOLS/MANUALS
The New Extensionist Core Competencies for individuals
Following the publication of the New Extensionist, the GFRAS Consortium on Education and Training collected existing curricula used in different countries, conducted an analysis of the competencies that the curricula focused on and organised consultations with experts to identify the core competencies needed in extension today. The experts then agreed on a listing of core competencies that the New Extensionist professional should have. This brief has these details.
- Published in CAPACITY DEVELOPMENT
Value Chain Toolkit- Harnessing the Power of Markets to Drive Change
The Value chain tool kit provides methods to support male and female farmers in the “Build to Grow to Prosper” phases of the CRS Pathway to Prosperity (Figure 1). Through this work CRS is striving to achieve industry leadership in value chain service delivery and influence that is gender-sensitive. Value chain programming is now synonymous with agricultural development and CRS aims to adopt this approach across our project portfolio.
- Published in GUIDE/TOOLS/MANUALS, VALUE CHAIN / MARKETS
Toolkit for value chain analysis and market development integrating climate resilience and gender responsiveness
This toolkit intends to provide policy makers, planners, project developers, technical advisors and implementers at local, regional or national level, with good practices of climate-resilient and gender-responsive value chain development.1 It aims to act as a repository of relevant tools and methodologies for identifying relevant stakeholders and engaging with them to collect data and analyse it to design interventions. Climate change threatens agricultural value chains and having a genderresponsive value chain approach is useful in analysing the climate risks, as it looks at stages during and beyond production, while using a more systemic approach to risk management.
- Published in GUIDE/TOOLS/MANUALS, VALUE CHAIN / MARKETS
Agricultural Extension and Advisory Services in Support of Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation: An Evidence Review
Agricultural extension and advisory services (EAS) is an umbrella term that refers to organizations, individuals and activities that supply information and services required by farmers and other agricultural actors to develop their own technical, organizational, and managerial capacities for livelihoods and well-being improvement. Public and private sector EAS are on the frontline in supporting smallholder farmers to adapt to the changing climate as they engage in field level activities and work closely with farmers to provide new technologies, technical information, knowledge, and skills, as well as linking them to other rural actors. EAS also work with policy makers and development program implementers to disseminate information about and put into practice new agricultural interventions, programs, and policies.
- Published in CLIMATE CHANGE
Climate Change and Agricultural Extension and Advisory Services
Rising temperatures, longer droughts, more severe storms, warming oceans, and recurring floods are already threatening global agriculture and food security. Most smallholder farmers in middle- and lowincome countries have limited abilities to respond and adapt to these climate risks. While highly vulnerable to climate change, agriculture is also a major source of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To strengthen the resilience of agriculture to changing climate, a two-pronged approach that supports adaptation – adjusting to actual or expected future climate change – and promotes mitigation – reducing greenhouse gases or enhancing accumulation and storage of GHG – is needed. Promoting these strategies at scale involves changing the behavior, strategies, and agricultural practices of millions of agricultural producers.
This brief discusses policy-level changes to enhance and strengthen the role and functioning of extension and advisory services (EAS) in addressing climate change adaptation and mitigation.
- Published in CLIMATE CHANGE
Upscaling Climate Smart Agriculture: Lessons for Extension and Advisory Services
Upscaling Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) entails changing the behavior, strategies and agricultural practices of millions of agricultural producers. Extension and Advisory Services (EAS) can play a very important role in upscaling CSA, but they need to be better organised to do so. This paper explores how EAS should be organized to support the upscaling of CSA by drawing lessons for EAS from four successful cases namely: natural resource management, crop management, varietal improvement and weather insurance. It used the Innovation Management Framework which identifies three elements that are critical for innovation: functions, actions and tools. To contribute fully to upscaling CSA, the paper argues that EAS providers need to broaden their mandate, partner with other relevant actors in the Agricultural Innovation Systems (AIS), deepen their level of engagement with the research, prepare for a long-term effort and seek to influence the enabling environment through policy advocacy
- Published in CLIMATE CHANGE
WOMEN AT THE HELM: Navigating the Digital Landscape of Agriculture
The study identified two types of enterprises led by women in the digital ecosystem: digitech enterprises, often founded by women with a background in technology, and digitally enabled enterprises, leveraging various digital technologies to promote their businesses. The majority of women entrepreneurs operate digitally enabled enterprises, reflecting the tech-driven nature of modern agribusiness.
This compilation of interviews illustrates how digital innovations support women agripreneurs in India, showcasing their entrepreneurial journeys, aspirations, challenges, and strategies to overcome these challenges through digital interventions and other forms of support. It is intended to benefit those supporting women agripreneurs, particularly within India’s agribusiness incubation centres, offering valuable insights and lessons for leveraging digital innovations to enhance enterprise performance. We sincerely believe that each of these life stories will also inspire several budding women agripreneurs and help them assess their digital capacity gaps and take steps to address these.
- Published in POLICY
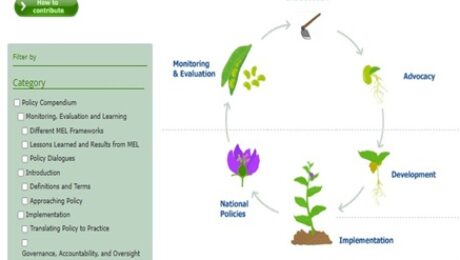
GFRAS Policy Compendium
The Policy Compendium is a tool that contributes to filling the gap between the rural advisory services (RAS) policy environment and RAS efforts in the field. It helps direct decisions and facilitate successful policy processes and outcomes in extension and advisory services by making knowledge accessible, fostering synergies and promoting policy processes to improve RAS and rural development.
- Published in POLICY
Agricultural Extension and Advisory Services: Serving Farming Community by Agripreneurship Amid COVID-19
The COVID-19 outbreak has generated extreme vulnerability in the agriculture sector by creating a
future threat to food security. The Agricultural Extension and Advisory Service (EAS) systems have
been playing a crucial role at the frontline of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic in rural areas.
This is not the first time that EAS has been called to intervene in an emerging catastrophe. As an
institution with trained technical staff, the extension has supported efforts and educated
communities during natural disasters. Agripreneurs trained under the AC & ABC scheme have
changed their way of operating in order to adapt to the government regulations. Efforts by MANAGE
and partners have resulted in the training of 72,806 agri-graduates and the establishment of 30,583
(42%) active agriventures across the world as of 2 December 2020. Although the pandemic has
affected the agripreneurs’ business in terms of getting recommended inputs, reduced sale of inputs
and monthly turnover, their extension services have remained significant.
- Published in AGRIPRENEURSHIP